Laser cutting is a highly efficient, precise, and flexible processing method, widely used in automotive, aerospace, construction machinery, and heavy equipment manufacturing. Although laser cutting machines continue to advance, common problems may still occur in actual production, leading to reduced cutting quality, lower efficiency, or increased costs.
Based on extensive industry experience, Han's Laser has summarized the most common laser cutting problems and solutions, providing practical references for operators and manufacturers. Whether you are using an entry-level low-power laser cutter or a high-end, high-power laser cutting system, the following guidelines will help you improve cutting quality and productivity.
1. Burrs or Rough Edges on Cutting Surface
Symptoms: Rough or uneven cut edges with burrs or jagged lines.
Possible Causes:
-
📌Insufficient laser power to fully melt the material
-
📌Cutting speed too fast, not enough time to complete the cut
-
📌Incorrect focal point position, reducing energy density
-
📌Improper assist gas pressure, slag not blown away
-
📌Using one parameter setting for all materials without adjustment
-
📌Contaminated optical components (lens or nozzle)
Solutions:
-
☑️Increase laser power and reduce cutting speed
-
☑️Recalibrate the focus, keeping it slightly below the material surface
-
☑️Adjust assist gas pressure for smoother slag removal
-
☑️Set parameters according to material type and thickness
-
☑️Regularly clean lenses, nozzles, and mirrors to maintain beam quality
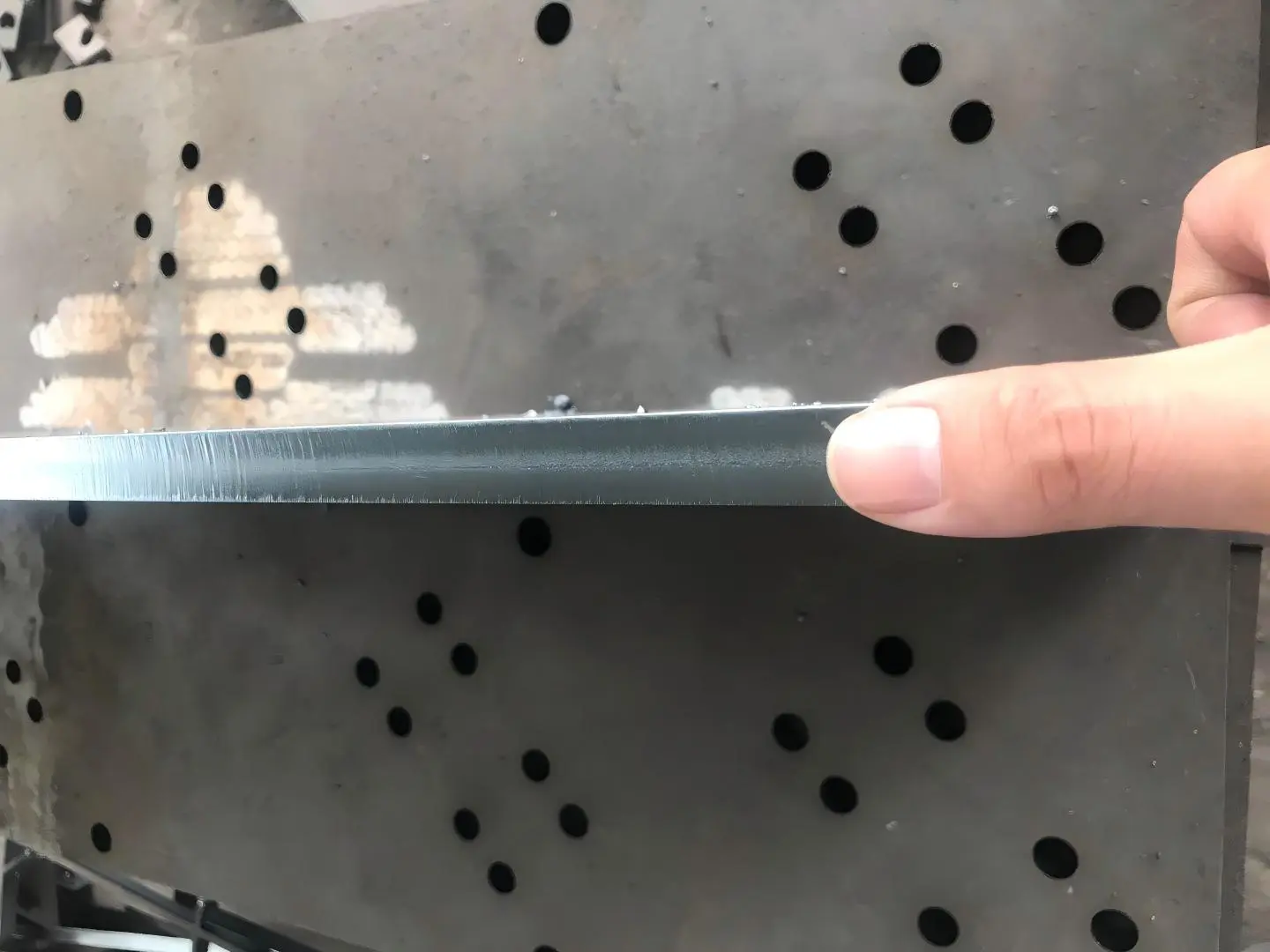

2. Excessive Melting or Wide Kerf
Symptoms: Cut lines are wider than expected, edges appear overheated or melted.
Possible Causes:
-
📌Laser power too high, causing overheating
-
📌Cutting speed too slow, leading to heat accumulation
-
📌Incorrect focus or nozzle height
-
📌Low assist gas flow
-
📌Thick materials or poor thermal conductivity
-
📌Poor beam quality or instability
Solutions:
-
☑️Reduce power settings according to material thickness
-
☑️Increase cutting speed to minimize heat exposure
-
☑️Recalibrate focus and nozzle height
-
☑️Ensure stable and sufficient gas supply
-
☑️Optimize parameters for thick or difficult-to-process materials
-
☑️Regularly check laser source and beam path
3. Uneven Cutting Surface or Wavy Edges
Symptoms: Wavy patterns, inconsistent smoothness on cut surfaces.
Possible Causes:
-
📌Unstable laser power output
-
📌Uneven cutting speed
-
📌Focal point drift
-
📌Warped or uneven material sheets
-
📌Machine vibrations or loose components
-
📌Irregular assist gas flow
Solutions:
-
☑️Use a stable power source and ensure consistent output
-
☑️Maintain steady cutting speed
-
☑️Regularly calibrate focusing system
-
☑️Level and fix material sheets before cutting
-
☑️Tighten mechanical parts and check guide rails
-
☑️Use flow regulators to stabilize gas pressure
4. Abnormal Sparks During Cutting
Symptoms: Excessive or irregular sparks during cutting.
Possible Causes:
-
📌Laser power too high
-
📌Cutting speed too slow, causing overheating
Solutions:
-
☑️Reduce laser power settings
-
☑️Increase cutting speed to minimize thermal stress
5. Incomplete Cutting or Penetration Failure
Symptoms: Workpiece not fully separated, partial bonding remains.
Possible Causes:
-
📌Insufficient laser power
-
📌Cutting speed too fast
-
📌Contaminated lens or nozzle
-
📌Incorrect focal point
-
📌High-reflective materials (aluminum, stainless steel)
Solutions:
-
☑️Increase power settings
-
☑️Reduce cutting speed
-
☑️Clean or replace optical components
-
☑️Re-adjust focal point
-
☑️Pre-clean or treat reflective material surfaces

6. Burn Marks or Discoloration on Edges
Symptoms: Brown, yellow, or black discoloration along cut edges.
Possible Causes:
-
📌Excessive heat input or power
-
📌Oxygen cutting accelerates oxidation
-
📌Cutting speed too slow
Solutions:
-
☑️Lower power or switch to pulsed cutting mode
-
☑️Use nitrogen or argon assist gas instead of oxygen
-
☑️Increase cutting speed for cleaner edges
7. Slag Accumulation at Bottom of Cut
Symptoms: Hardened slag beads at the underside of the cut.
Possible Causes:
-
📌Insufficient assist gas pressure
-
📌Cutting speed too slow or laser power too low
-
📌Incorrect nozzle gap or height
Solutions:
-
☑️Increase assist gas pressure and flow
-
☑️Adjust cutting speed and power based on material type
-
☑️Optimize nozzle height for better gas flow and beam convergence
8. Piercing Issues at Start of Cutting
Symptoms: Laser struggles to pierce through material at the beginning.
Possible Causes:
-
📌Incorrect piercing parameters (time or power)
-
📌Unstable laser beam
-
📌Dirty or oxidized material surface
Solutions:
-
☑️Extend piercing time or use step-by-step piercing
-
☑️Stabilize beam source
-
☑️Clean material surface before cutting
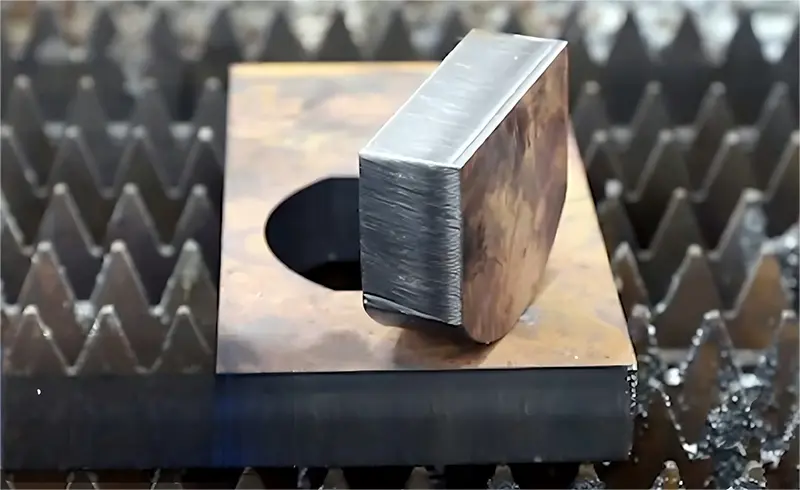
Conclusion
Laser cutting offers unmatched precision, efficiency, and flexibility in industrial manufacturing. However, cutting quality largely depends on fine-tuning process parameters, regular equipment maintenance, and material characteristics. From burrs and burn marks to penetration failure, most issues can be resolved with proper adjustments and preventive measures.
As a global leader in laser technology, Han's Laser provides customers with advanced laser cutting solutions, comprehensive training, and responsive technical support to help achieve higher productivity and lower operating costs.



















 Previous
Previous

 LET’S TALK
LET’S TALK