







-
Conversation
 Conversation
Conversation
 We're online!What kind of machine are you looking for?What kind of machine are you looking for?
We're online!What kind of machine are you looking for?What kind of machine are you looking for? -



-
sales01@hanslaser.com

-
Bevel cutting—the process of creating angled edges on metal plates or pipes—is a critical step in modern manufacturing. Beyond aesthetics, beveled edges improve wear resistance, enhance weld quality, and make components safer and easier to handle. With fiber laser technology, bevel cutting has become faster, cleaner, more precise, and easily integrated into automated production lines.
What is Bevel Cutting?
Bevel cutting refers to creating an angled edge along the end or side of a workpiece, typically up to ±45°. Unlike standard 90° cuts, bevels introduce a slope that is both functional and visually appealing.
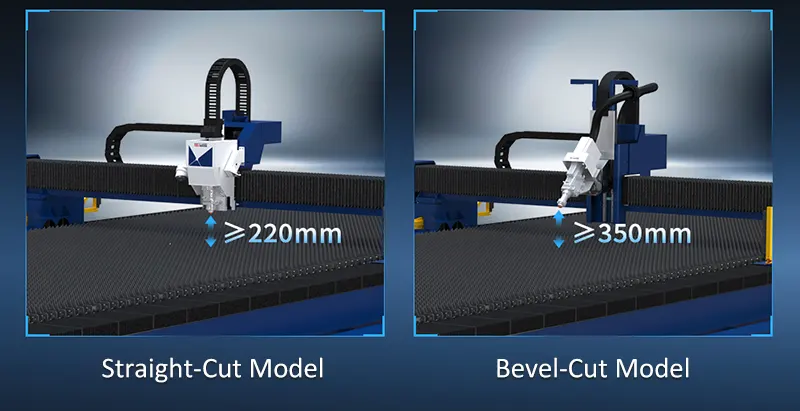
Advantages of Bevel Cutting:
-
Weld Preparation: Increases bonding area for stronger welds.
-
Safety: Reduces sharp edges for safer handling.
-
Aesthetic Finish: Provides smooth and refined edges.
-
Durability: Even stress distribution enhances component lifespan.
For pipes, proper beveling ensures high-quality weld joints, reducing risks of leaks and structural failures. Modern fiber laser systems can cut and bevel in a single pass, saving time and eliminating secondary processing.
Common Bevel Types
-
V-Cut (Top Bevel): Downward slope, commonly used for welding prep.
-
A-Cut (Bottom Bevel): Upward slope, suitable when the workpiece is flipped.
-
X-Cut (Top & Bottom Bevel): Forms a wedge-shaped edge.
-
Y-Cut (Chamfer): Partial bevel for edge smoothing.
-
K-Cut (Double Chamfer): Ideal for welding and precise assembly.

Plate vs. Tube Bevel Cutting
Plate Bevel Cutting:
-
Rotating laser heads can achieve ±45° high-precision bevels in one pass without repositioning.
-
Widely used in shipbuilding, pressure vessel manufacturing, and steel structures.
Tube Bevel Cutting:
-
Laser systems adapt to curved surfaces and circular profiles.
-
Capable of saddle cuts, fish-mouth joints, and complex angled bevels.
-
Common in piping systems, chassis construction, and building frameworks.
Why Laser Bevel Cutting Outperforms Traditional Methods
Traditional beveling methods—manual grinding, plasma cutting, and portable beveling machines—have limitations:
-
Inconsistent angle precision
-
High dependency on operator skill
-
Secondary deburring or cleaning required
-
Limited automation potential
Fiber Laser Bevel Cutting Advantages:
-
One-Step Process: No flipping or repositioning needed.
-
High Precision & Repeatability: Narrow kerf and controllable laser energy deliver accurate bevels.
-
Flexible Production: Suitable for both small and large batch runs.
-
Direct Welding Prep: Clean edges eliminate post-processing.
Applications of Bevel Cutting
-
Pipe Welding: Oil & gas, chemical plants, and construction pipelines.
-
Steel Structures: Bridges, rail systems, and heavy machinery.
-
Sheet Metal Fabrication: Deburring and edge finishing.
-
Machinery & Automotive: Strong weld joints for load-bearing parts.
-
Custom Design: Decorative edges or specialized functional components.
Conclusion
Bevel cutting is no longer a bottleneck in metal processing. From manual grinding and plasma cutting to advanced fiber laser systems, modern technology improves precision, efficiency, and safety. Whether for plates or pipes, automated laser bevel cutting delivers high-quality, consistent results in a single operation.
Contact Han's Laser We provide fiber laser bevel cutting systems suitable for a wide range of materials, helping manufacturers improve productivity, reduce costs, and maintain consistent quality with every cut.



-
Products + -
-
Company + -
-
Fast entry + -
Disclaimers
Please read these terms carefully before using our site. By using this site, you agree to the terms contained herein and that you have the legal authority to accept these terms. If you do not agree with the terms, you should not use our site. Furthermore, we reserve the right to change the terms of use at any time, without prior notice. If you are using the site after we post a change, you accept that change. You should check these terms periodically.
We have made every effort to present the content on the website accurately, but additions, modifications, and changes may occur.
This Terms of Use contains the following topics:
• Warranties
• Copyright
• Links to Third Party Websites
• Disclaimer
• Contact Us
Warranties
This website content is provided “as is” without warranties of any kind, either expressed or implied, including but not limited to the implied warranties of merchantability, fitness for a particular purposes, or non-infringement.
Copyright
All copyrights, trademarks and all other intellectual property rights in the website and its content (including without limitation the Website design, text, graphics and all software and source codes connected with the Website) are owned by or licensed to Han’s Laser or otherwise used by Han’s Laser as permitted by law.
In accessing the website, you agree that you will access the content solely for your personal, non-commercial use. None of the content may be downloaded, copied, reproduced, transmitted, stored, sold or distributed without the prior written consent of the copyright holder. This excludes the downloading, copying and/or printing of pages of the Website for personal, non-commercial home use only.
Links to Third Party Websites
Han's Laser does not review or control third party websites that link to or from our website, is not responsible for their content, and does not represent that their content is accurate or appropriate. Han’s Laser makes no representations or warranties with respect to any linked site: use of any linked site is solely at your own risk.
Disclaimer
In no event shall Han’s Laser or any of its affiliate, or the officers, directors, employees, members, or agents of each of them, be liable for any damages of any kind, including without limitation any special, incidental, indirect, or consequential damages, whether or not advised of the possibility of such damages, and on any theory of liability whatsoever, arising out of or in connection with the use of performance of this website.
Privacy Policy
Welcome to Han’s Laser Privacy Policy page. Han’s Laser is committed to protecting your privacy. When you use Han’s Laser website services, you trust us with your information. This Privacy Policy is meant to help you understand what data we collect, why we collect it, and what we do with it. We hope you will take time to read it carefully.
This Privacy Policy contains the following topics:
• Information Collected
• Purpose of Using Personal Data
• Usage of Personal Data by the Company
• Links & Disclaimer
• Contact Us
Information Collected
Han’s Laser will not obtain personally-identifying information about you when you visit our site, unless you choose to provide such information to us.
We may receive and/or collect Personal Data in the following ways:
1.Personal data you provide to us on our site.
If you send us a “Contact Us” request or feedback, or if you seek information about our products, services, and prices, or in connection with purchasing a product or service, you may be required to provide us with certain personal data, such as:
Your name;
Email address;
Communications you send to us.
We may also ask you to provide additional information, such as company name or industry.
2.Information collected automatically.
Certain information on our site is collected automatically by means of various software tools. We have a legitimate interest in using such information to assist in log-in, systems administration purposes, information security and abuse prevention, to track user trends, and to analyze the effectiveness of our Site. Alone or in combination with other information, such automatically collected information may constitute Personal Data. Some of our service providers may use cookies or other methods to gather information regarding your use of our Site. Such third parties may use these cookies or other tracking methods for their own purposes by relating information about your use of our Site with any Personal Data about you that they may have. The use of such information by a third party depends on the privacy policy of that third party.
① Log Files. The information inside the log files includes internet protocol (“IP”) addresses, type of browser, Internet Service Provider (ISP), date/time stamp, referring/exit pages, clicked pages and any other information your browser may send to us.
② Cookies. We use cookies to make interactions with our site easy and meaningful. When you visit our Site, our servers may send a cookie to your computer. Standing alone, cookies do not personally identify you; they merely recognize your web browser.
We may use cookies that are session-based and persistent-based. Session cookies exist only during one session. They disappear from your computer when you close your browser software or turn off your computer. Persistent cookies remain on your computer after you close your browser or turn off your computer. Please note that if you disable your web browser’s ability to accept cookies, you will be able to navigate our Site, but you may not be able to successfully use all of the features of our Site.
③ Other Tracking Technologies. When you visit our Site, we may collect your IP addresses to track and aggregate non-Personal Data. For example, we may use IP addresses to monitor the regions from which you navigate our Sites.
We may also use web beacons alone or in conjunction with cookies to compile information about your usage of our Site and interaction with emails from us. Web beacons are clear electronic images that can recognize certain types of information on your computer, such as cookies, when you viewed a particular site tied to the web beacon. For example, we may place web beacons in marketing emails that notify us when you click on a link in the email that directs you to our site. We may use web beacons to operate and improve our site and email communications.
④ Analytics Software Tools. We use Google Analytics on our Site to help us analyze the traffic on our Site. For more information on Google Analytics’ processing of Personal Data, please see: https://policies.google.com/technologies/partner-sites. By using a browser plugin: http://www.google.com/ads/preferences/plugin/, provided by Google, you can opt out of Google Analytics.
Purpose of Using Personal Data
If you submit or we collect Personal Data through our Site, then such Personal Data may be used in the following ways:
to analyze, administer, and improve our Site and services;
to contact you in connection with our Site and certain services, notifications, events, programs or offerings that you may have registered for;
to send you updates and promotional materials that you have registered for;
to protect our rights and/or our property and to ensure the technical functionality and security of our site.
Usage of Personal Data by the Company
We do not sell, lease, rent or otherwise disclose the Personal Data collected from our Site to third parties unless otherwise stated below or with your consent.
① By Law to Protect Right.
We may share your information as permitted or required by any applicable law, rule or regulation under the following conditions: If we have a good-faith belief that the release of information about you is necessary to comply with any applicable law, regulation, legal process or governmental request; to investigate or remedy potential violations of our policies; or to protect the rights, property, and safety of others.
② Third-Party Service Providers.
We may share your information with third parties that perform services for us or on our behalf. This could include data analysis, email delivery, hosting services, customer service, and marketing assistance.
③ Affiliates.
We may share your information with our affiliates which may include our subsidiaries, joint venture partners or other companies that we control or that are under common control with us. In this case we will require those affiliates to honor this Privacy Policy.
④ Merger, Sale or Change of Control.
If we reorganize or sell all or a portion of our assets, undergo a merger, or are acquired by another entity, we may transfer your information to the successor entity.
Links & Disclaimer
Our website has links to many other organizations with their permission. Upon leaving the Han’s Laser website, you are subject to the privacy policy of the new site. Han’s Laser is not responsible for the availability of the systems being linked to and these links are provided to you as a service for you to better understand the different business relationships that Han’s Laser has established.
Contact Us
If you have questions or comments about this Privacy Policy, please contact the Company at email: sales01@hanslaser.com or contact the Company at:
Han’s Laser
HeadOffice Address: Shenzhen Han’s Laser Technology Co., Ltd. Chongqing Road, Bao’an District, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
Telephone:(+86) 135 3781 5660
Han’s Laser Cookie Policy
Han’s Laser uses cookies to provide various services, continuously optimize the user experience, and display relevant advertisements based on visitors’ interests.
By clicking "Accept All Cookies," you agree to the use of cookies on hansme.net and its subpages and allow us to process your data.
For more details, please refer to the Privacy Policy.






 Previous
Previous

 LET’S TALK
LET’S TALK