Selecting the proper laser power is one of the most important decisions in metal cutting. The right power level directly affects cutting quality, productivity, operating cost, and long-term machine performance. Too little power leads to poor penetration and slow cutting speeds, while excessive power can cause edge burning, distortion, and unnecessary energy consumption.
This guide explains how to choose laser power based on material type, thickness, cutting speed requirements, and edge quality expectations—helping you make a practical and cost-effective decision.
1. Know How Different Metals React to Laser Cutting
Each metal behaves differently during laser cutting due to variations in reflectivity, thermal conductivity, and melting temperature. Understanding these characteristics is the first step in choosing the correct laser power.
Mild Steel (Carbon Steel)
Mild steel is one of the easiest materials to cut with a laser. Its relatively low thermal conductivity allows efficient heat concentration.
-
Up to 6 mm: 1,000W–3,000W
-
6–20 mm: 4,000W or higher
Lower power works well for thin sheets, while thicker plates require more power to maintain cutting stability and edge consistency.
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel absorbs laser energy more effectively than aluminum or copper, making it suitable for a wide range of laser powers.
-
Up to 5 mm: Around 1,000W
-
6–15 mm: 2,000W–4,000W
Higher power improves cutting speed and reduces slag formation on thicker stainless steel.
Aluminum
Aluminum presents more challenges due to its high reflectivity and excellent heat dissipation.
-
Up to 12 mm: 2,000W–4,000W
-
Thicker plates: Up to 6,000W may be required
Fiber lasers are typically preferred for aluminum cutting to ensure stable performance.
Copper and Brass
Copper and brass are highly reflective materials, requiring careful laser selection and sufficient power.
-
Recommended minimum: 2,000W
-
Thicker materials: 4,000W or more
High-power fiber lasers with proper protection are essential to cut these materials safely and efficiently.

2. Match Laser Power to Material Thickness
Material thickness is a key factor when determining laser power requirements.
Thin Sheets (1–5 mm)
Thin materials can be cut efficiently with lower power levels.
-
Recommended power: 500W–2,000W
-
Benefits include lower energy consumption, minimal heat distortion, and clean edges.

Medium Thickness (6–12 mm)
For medium-thickness metal sheets, higher power ensures stable cutting speed and consistent quality.
-
Recommended power: 2,000W–4,000W
This range is commonly used for stainless steel and aluminum in industrial applications.
Thick Plates (13 mm and above)
Thick metal plates demand high laser power to achieve full penetration and reliable cutting.
-
Recommended power: 4,000W–6,000W or higher
High power reduces cutting time and minimizes burrs or incomplete cuts.
3. Balance Cutting Speed and Precision
Laser power directly influences cutting speed and accuracy. The ideal balance depends on your production goals.
Lower Power for High Precision
For applications involving fine contours, small holes, or detailed patterns, lower power is often preferable.
-
Typical range: 500W–1,000W
-
Advantages include reduced thermal impact, smoother edges, and better dimensional accuracy.
Higher Power for Maximum Productivity
In high-volume production environments, cutting speed becomes a priority.
-
Typical range: 3,000W–6,000W
-
Higher power enables faster processing of thicker materials without compromising cut quality.
4. Consider Edge Quality Requirements
Edge quality is a critical factor, especially when parts require minimal post-processing.
Thick Materials
Higher power helps maintain smooth edges and reduces slag and burr formation when cutting thick steel or aluminum.
Thin Materials
Excessive power on thin sheets can cause edge burning or warping. Lower power settings provide better control and cleaner results.
5. Energy Efficiency and Cost Optimization
Laser power selection also affects operating costs and return on investment.
Lower Power for Cost Control
If your production mainly involves thin sheets, a lower power machine (1,000W–2,000W) can significantly reduce energy consumption and maintenance costs.
Higher Power for Heavy-Duty Production
For thick materials and continuous operation, higher power systems (4,000W–6,000W) offer better long-term efficiency through faster cutting speeds and reduced secondary processing.
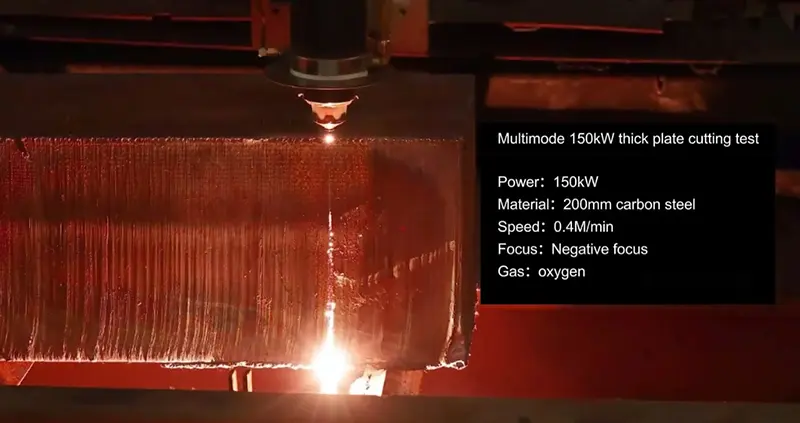
Conclusion
Choosing the right laser power for metal cutting is about finding the best balance between material type, thickness, speed, edge quality, and operating cost. The correct power level improves productivity, ensures consistent cut quality, and helps avoid unnecessary energy waste.
Whether you are cutting thin aluminum sheets or thick steel plates, selecting the appropriate laser power is essential for reliable and efficient performance.
If you need professional guidance on laser power selection or machine configuration, Han's Laser offers customized laser cutting solutions backed by extensive industry experience. Our technical team is ready to help you find the optimal system for your specific application.





















 Previous
Previous

 LET’S TALK
LET’S TALK